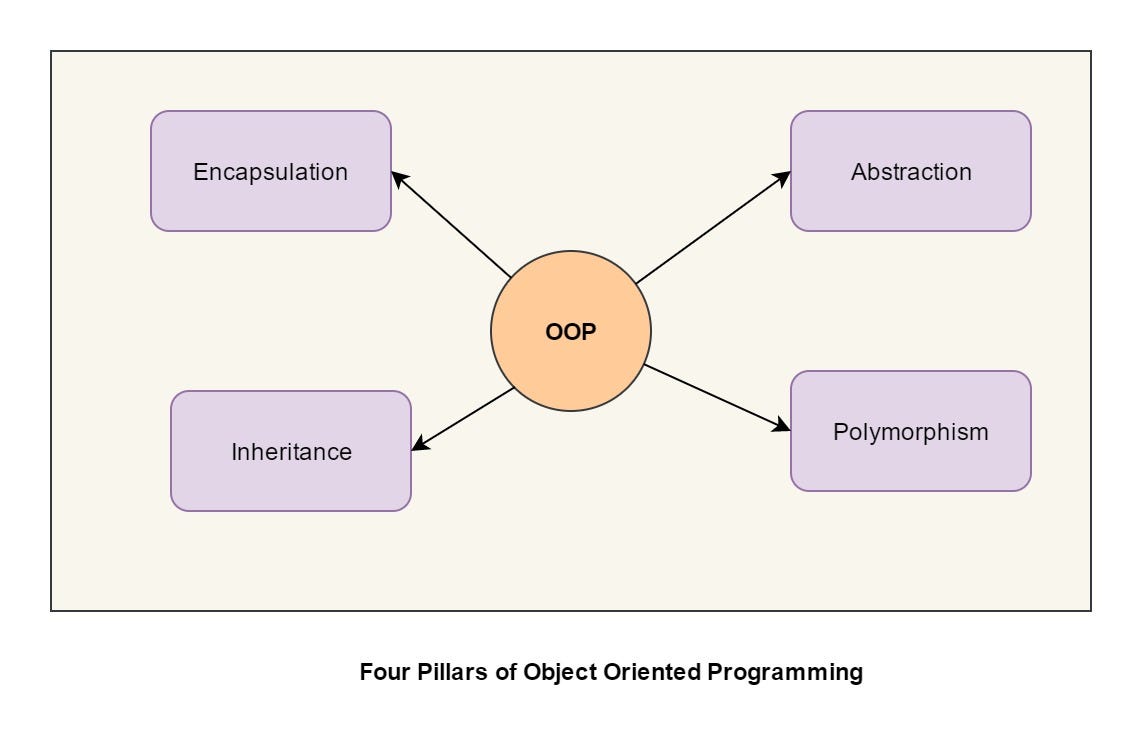
what is Inheritance?
In OOP, the concept of inheritance allows a class to accept or have the properties of another class (inherited). A sub-class or derived class is a class that inherits the characteristics/methods of another class. Heritage reduces code redundancy, allowing the class to use other class methods without having to rewrite the code. This allows for dynamic programming using the main class’s methods (also called the parent class). A subclass has the same properties as a primary class, but it can also have additional methods that are either completely independent or not present in the main class.
What is the Function of Inheritance?
Children’s classes may be built to enhance the parent’s class functionality and add more characteristics once essential properties and behaviors have been defined in the parent’s class.
Example:-
This distinction is demonstrated by creating a parent class child class(HerdingDog) (Dog) and then adding a single herd() behaviour.
The following code shows how the child class (HerdingDog) inherits a parent class method (bark) (Dog), and the child class adds an extra method herd().
When the code uses the fluffy.bark() function, the method bark() travels up the child’s chain to find out where the bark method is declared.