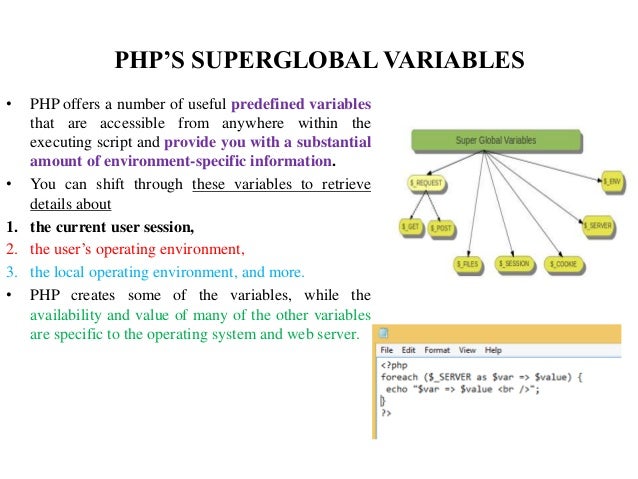
What is $_SERVER?
It’s a super global variable in PHP that keeps track of headers, paths, and script locations. Some of these components are used to obtain data from the $_SERVER super global variables.
Example:-
Output:-

To retrieve some information, we used the $_SERVER components in the code above. Using the ‘PHP SELF’ element, we retrieve the current file name that is being worked on. Then, using the ‘SERVER NAME’ attribute, we retrieve the current server name. Then we use ‘HTTP HOST’ to retrieve the host name.
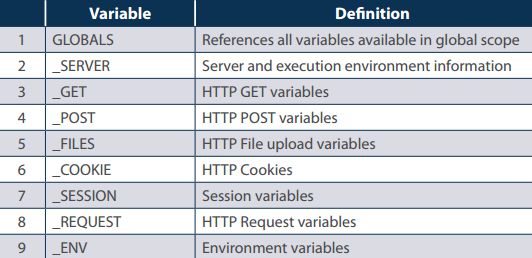
The following table lists the most important elements that can go inside $_SERVER:
| Element/Code | Description |
|---|---|
| $_SERVER[‘PHP_SELF’] | Returns the filename of the currently executing script |
| $_SERVER[‘GATEWAY_INTERFACE’] | Returns the version of the Common Gateway Interface (CGI) the server is using |
| $_SERVER[‘SERVER_ADDR’] | Returns the IP address of the host server |
| $_SERVER[‘SERVER_NAME’] | Returns the name of the host server (such as www.w3schools.com) |
| $_SERVER[‘SERVER_SOFTWARE’] | Returns the server identification string (such as Apache/2.2.24) |
| $_SERVER[‘SERVER_PROTOCOL’] | Returns the name and revision of the information protocol (such as HTTP/1.1) |
| $_SERVER[‘REQUEST_METHOD’] | Returns the request method used to access the page (such as POST) |
| $_SERVER[‘REQUEST_TIME’] | Returns the timestamp of the start of the request (such as 1377687496) |
| $_SERVER[‘QUERY_STRING’] | Returns the query string if the page is accessed via a query string |
| $_SERVER[‘HTTP_ACCEPT’] | Returns the Accept header from the current request |
| $_SERVER[‘HTTP_ACCEPT_CHARSET’] | Returns the Accept_Charset header from the current request (such as utf-8,ISO-8859-1) |
| $_SERVER[‘HTTP_HOST’] | Returns the Host header from the current request |
| $_SERVER[‘HTTP_REFERER’] | Returns the complete URL of the current page (not reliable because not all user-agents support it) |
| $_SERVER[‘HTTPS’] | Is the script queried through a secure HTTP protocol |
| $_SERVER[‘REMOTE_ADDR’] | Returns the IP address from where the user is viewing the current page |
| $_SERVER[‘REMOTE_HOST’] | Returns the Host name from where the user is viewing the current page |
| $_SERVER[‘REMOTE_PORT’] | Returns the port being used on the user’s machine to communicate with the web server |
| $_SERVER[‘SCRIPT_FILENAME’] | Returns the absolute pathname of the currently executing script |
| $_SERVER[‘SERVER_ADMIN’] | Returns the value given to the SERVER_ADMIN directive in the web server configuration file (if your script runs on a virtual host, it will be the value defined for that virtual host) (such as someone@w3schools.com) |
| $_SERVER[‘SERVER_PORT’] | Returns the port on the server machine being used by the web server for communication (such as 80) |
| $_SERVER[‘SERVER_SIGNATURE’] | Returns the server version and virtual host name which are added to server-generated pages |
| $_SERVER[‘PATH_TRANSLATED’] | Returns the file system based path to the current script |
| $_SERVER[‘SCRIPT_NAME’] | Returns the path of the current script |
| $_SERVER[‘SCRIPT_URI’] | Returns the URI of the current page |