What is Loop?
A loop is an Iterative Control Structure that requires the same number of codes to be executed several times until a specific condition is met. When writing code, you may want a specific block of code to run a certain number of times. As a result, rather than applying nearly similar code lines to a script, we can employ loops.
What are the Different types of Loops?
Loops are used repeatedly to run the same piece of code as long as a given condition is met. A loop’s basic premise is to simplify recurring procedures in a programmer in order to save time and effort. PHP supports four different loop styles.
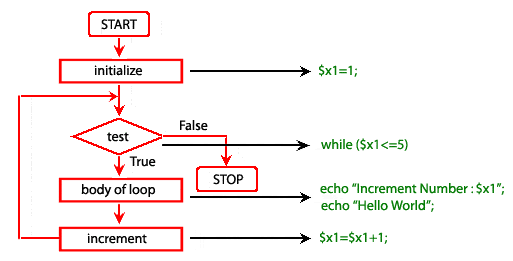
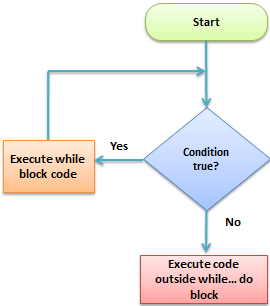
while – Loops through a code block as long as the given condition is true.do...while – The code block running once and then is tested. State. If the condition is true, the declaration shall be repeated until the condition stated is true.for – Loops via a code block before a given number is reached in the counter.foreach – Loops for each unit of an array across a block of code.
Why to Use Loops?
When trying to recreate code, it might be tedious to retype or copy and paste the same code over and over again. Worse, unintentional mistakes might lead to programme malfunctions.
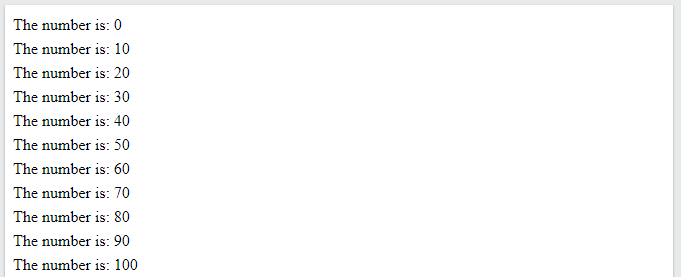
That’s quite a few keystrokes! What if you decide later that you want to start each statement with “The count is currently: ”? You’d have to copy it and paste it into every single line.
Fortunately, loops are a function in most programming languages that allows you to automatically repeat code before such requirements are met. Iteration is a phrase used to describe the repetition of code, and it refers to each time the code is executed. Loops will reduce the number of lines of code you write while still allowing you to update it later.
PHP is no exception, as it offers a variety of ways to repeat the execution of a code block.
This Article has cover the following PHP loop types:
whiledo … whileforforeach
There are conditions in each of these loops that prevent the loop from executing. If these requirements are not met, an endless loop will follow, and the software will never be able to quit executing the code block.
How to use loops in PHP?
In order to write effective code, any programmer needs have a thorough understanding of loops and how to use them effectively in programming.
When writing code, we must always repeat a same set of functions. Performing them one at a time would result in a higher number of lines of code and a longer duration. As a result, the software gets more difficult to understand. As a result, instead of using loops to run the code, we can use them!
Tagged : Different types of Loops / How / How to use loops in PHP / loop / loops in PHP / Php / php loops / Tutorials for PHP Loops / types of Loops / use loops in PHP / Use of Loops / What / What is Loop / Why / Why to Use Loops